What is Hieroglyphics? Ancient Egyptian Writing Explained
What is Hieroglyphics? Ancient Egyptian Writing Explained
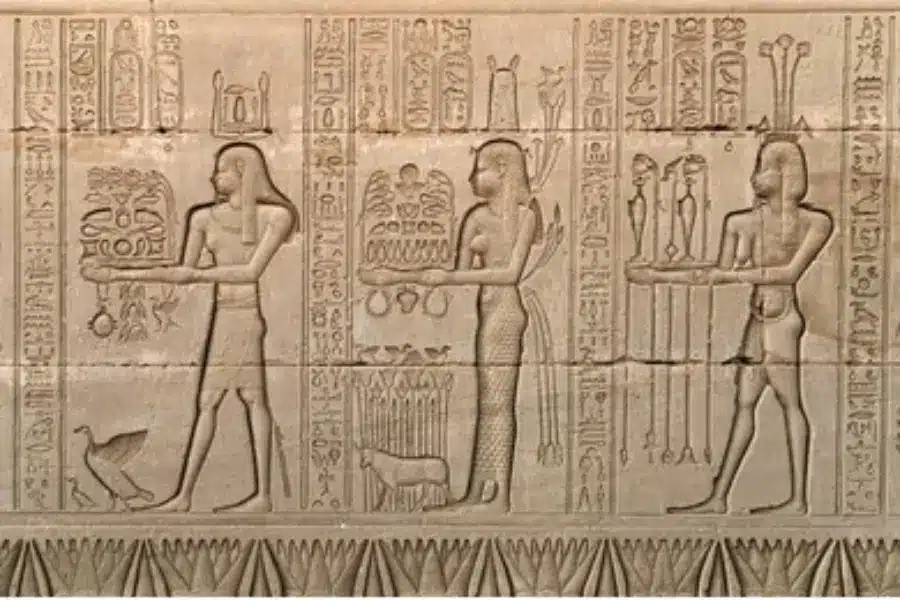
Have you ever toured an Egyptian temple or stood in front of an ancient obelisk? Have you noticed the carvings that seem to cover every single inch of their stone surfaces?
These carvings are hieroglyphics. So, what is hieroglyphics? It was the formal and widely used writing system of ancient Egypt, created to record everything from royal decrees to sacred prayers.
This unique way of writing relied on a rich collection of symbols and images, blending art with language to document daily life, religion, power, and belief. Hieroglyphic writing allowed the ancient Egyptians to preserve their thoughts and traditions in a form meant to last forever.
Seeing these carvings on the walls and columns of ancient monuments is one of the most meaningful ways to deeply connect with Egypt’s history, turning stone into a silent storyteller of a civilization that refused to be forgotten.
What Is Hieroglyphics
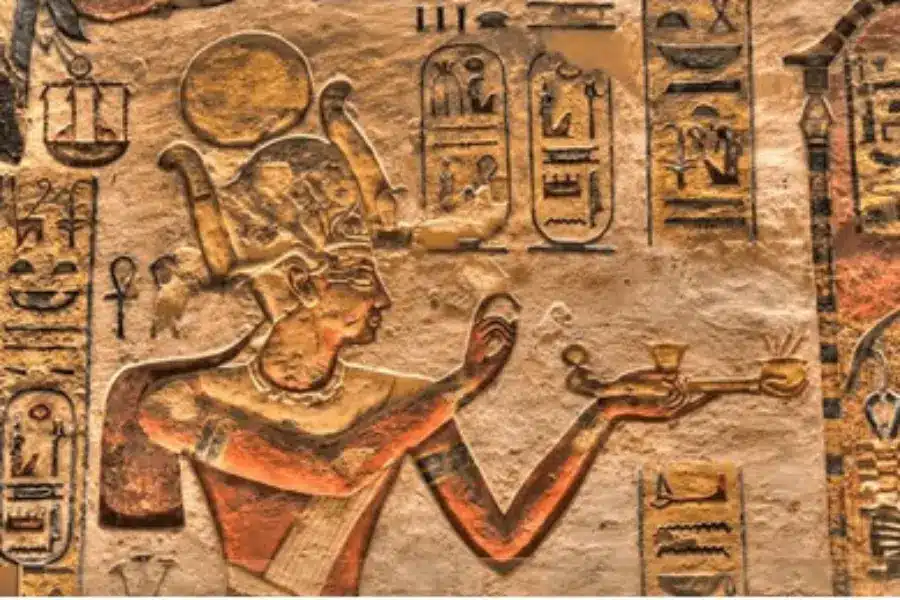
Hieroglyphs were the formal and widely used writing system of ancient Egypt, built from a complex mix of pictures and symbols. Unlike modern alphabets, these signs could represent specific sounds, complete words, or even abstract ideas, allowing the Egyptians to record their history, religion, and laws with remarkable detail and a unique artistic beauty.
Many people feel confused when trying to understand the difference between the terms hieroglyphs and hieroglyphics. The distinction is simple but important: hieroglyphs refer to the individual signs or characters themselves, while hieroglyphics describes the entire writing system that brings those signs together.
The word itself comes from the Greek term “hieroglyphika,” which literally means “sacred carvings.” This origin reflects how the ancient Egyptians viewed writing—not merely as a tool for communication, but as a divine gift from the god Thoth.
For the Egyptians, writing was meant to last for eternity, carved onto the walls of temples and tombs so that words, names, and prayers could survive forever. When you first look at a wall covered in these symbols, it may seem like a simple collection of images, but in reality, it is a highly sophisticated and carefully structured code.
- Hieroglyphs: Individual symbols that can represent sounds, words, or ideas.
- Hieroglyphics: The complete system of writing, using all the hieroglyphs together.
- Phonograms: Signs that represent a specific sound, similar to letters in our alphabet.
- Ideograms: Signs that represent the object or concept they depict.
These symbols, known as hieroglyphs, carry multiple layers of sound and meaning, which is exactly what makes the ancient Egyptian language so fascinating.
Hieroglyphics was not a simplified form of writing. It was a highly complex system that allowed the ancient Egyptians to express deep ideas, poetry, and even scientific observations with a level of precision and richness that continues to impress the world today.
When and Where Did Hieroglyphics Begin?
When it comes to the origins of ancient Egyptian writing, we need to go back to around 3200 BCE.
Hieroglyphics began in a very simple form, appearing on basic labels carved into jars or ivory tags used for trade, administration, and taxation.
Over time, these early and simple symbols gradually evolved into the complex writing system that we recognize today.
This long development shows that hieroglyphics has deep historical roots and a clear origin—it did not suddenly appear, but grew steadily over centuries.
What’s truly amazing about Egyptian hieroglyphs history is:
- The system stayed remarkably consistent for over 3,000 years.
- While other civilizations were constantly changing their scripts or adopting new ones, the Egyptians connected to their “sacred carvings” with a sense of pride and tradition.
- The system lasted so long because of the close connection between the Egyptians and the thought of eternity.
- Hieroglyphs were strongly linked to religion and monuments, making any change feel like changing their identity.
- Faster ways of writing, like Hieratic and Demotic, were developed for everyday use.
- Despite all these changes, hieroglyphics still shine as an inspiration for anything meant to last forever, surviving through dozens of dynasties and foreign invasions until the end of the Roman period.
Thanks to the slow, steady evolution, rather than a sudden break from the past, the language survived through dozens of dynasties and foreign invasions, right up until the end of the Roman period.
How Did Egyptian Hieroglyphs Work?
Ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs may seem like a complicated writing system at first. However, once you understand how they work, you begin to realize how unique and different they truly are.
Hieroglyphs are unlike the traditional alphabets we use today. They were not simply a tool for communication, but carried a deeper, spiritual meaning for the ancient Egyptians.
This writing system functions like a multi-layered puzzle, where different types of signs work together to form a clear and meaningful message.
Types of Hieroglyphic Signs The Egyptians used three main types of signs to get their point across:
- First, there are phonograms, which are symbols that represent sounds, much like letters in modern alphabets. For example, the image of an owl represents the “m” sound.
- Second, there are ideograms, where the symbol directly represents the object or idea it depicts. A picture of the sun, for instance, simply means “sun.”
- Third, the Egyptians used determinatives. These signs are placed at the end of a word and do not have a sound of their own. Instead, they clarify the meaning of the word by showing its category. For example, if you see a pair of walking legs at the end of a word, you know it relates to movement or travel.
A common misconception is that hieroglyphs are simply “pictures of things.” In reality, most hieroglyphic signs represent sounds, not objects.
The main reason behind this confusion is that the ancient Egyptians did not write vowels such as a, e, i, o, or u. Instead, they recorded only consonants. This is why, when people attempt to “speak” ancient Egyptian today, they often insert a neutral “e” sound between consonants to make the words pronounceable.
For example, a word written as “nfr”, which means beautiful or good, is commonly pronounced as “nefer” by modern scholars.
Hieroglyphics was a clever and highly effective blend of sound and symbol, allowing the ancient Egyptians to be remarkably precise in their writing—even without a traditional alphabet.
How Were Hieroglyphs Read?
- Follow the faces: Always read in the direction that human or animal figures are facing.
- Top to bottom: If symbols are stacked vertically, read the top symbol before the one beneath it.
- No spaces: Hieroglyphs are written in a continuous flow, without spaces between words or sentences.
One of the most distinctive features of hieroglyphics is its flexibility. Unlike English, which is always written from left to right, hieroglyphs could be written left to right, right to left, or even vertically.
The key to knowing exactly where to begin reading is simply to observe the living creatures within the text. If birds, people, or animals are facing left, you start reading from the left and continue toward their faces.
This freedom reflects the incredible creativity of ancient Egyptian artists. They often arranged text around doorways, statues, and architectural elements to achieve perfect balance and symmetry. In ancient Egypt, writing was not separate from art—it was an essential and beautiful part of it.
Who Could Read and Write Hieroglyphics?
In ancient Egypt, not everyone could read or understand hieroglyphics, even though these inscriptions appeared everywhere—on temple walls, columns, statues, and tombs.
It is estimated that only about 1% to 5% of the population was literate. Writing was a highly specialized and complex skill that required many years of intense training.
Those who mastered this skill were known as scribes, and they held a respected and intelligent position within society. Scribes in ancient Egypt were not required to perform heavy physical labor or serve in the army.
Instead, they played a vital role as the backbone of the government, responsible for recording taxes, legal documents, and sacred texts. Education was demanding and expensive, so it was generally reserved for the children of the elite or members of the royal family.
Scribes were often depicted in statues seated cross-legged with a papyrus scroll resting on their lap, calm and focused. This familiar image reflects the high level of respect they received.
For the average farmer or laborer, the carvings on temple walls were likely viewed as powerful and magical images rather than written texts they could understand.
In this way, hieroglyphics functioned as a “secret” language of the elite, created to preserve the knowledge of the gods and the glory of the pharaohs for eternity.
Where Can You See Hieroglyphs Today in Egypt?
Seeing hieroglyphs carved into stone walls or columns in person is a completely different experience from viewing them in photos. These inscriptions are deeply and precisely carved into walls and pillars, or beautifully painted in colors that have survived for thousands of years.
Some of the best places to see hieroglyphs are the great temples of Upper Egypt, such as Karnak Temple and Luxor Temple, where massive columns are literally covered with detailed stories of gods, kings, and sacred rituals.
In Luxor at the Valley of the Kings, the experience becomes even more personal. The tomb walls are filled with carefully written texts meant to guide the pharaoh through the journey of the afterlife.
At Egypt Tours Group, we often tell our guests that seeing hieroglyphs “in the wild” feels like walking through a giant open-air library. You’ll find them carved on towering obelisks pointing toward the sun and on the monumental gateways of temples such as Edfu Temple and Philae Temple.
Even the museums in Cairo are filled with stelae and statues bearing incredibly fine inscriptions. Seeing them up close allows you to notice the texture of the stone and the precision of the ancient scribes, making history feel far more real than any textbook ever could.
It is one of those true “bucket list” moments that creates a powerful connection to the people who built this remarkable civilization.
The Rosetta Stone and Deciphering Hieroglyphs
By the 4th century CE, the last ancient Egyptian temples had been closed. As a result, the ability to read hieroglyphs was gradually lost. The inscriptions carved on temple walls and towers became mysterious symbols with unknown meanings, and many people began to believe they were merely magical images rather than a true written language.
This remained the case for centuries, until the discovery of the Rosetta Stone in 1799 finally opened the door to understanding ancient Egyptian writing once again.
- In 1799, all of this misunderstanding began to come to an end when a group of French soldiers discovered a dark stone slab in a town called Rosetta.
- This stone, later known as the Rosetta Stone, became the key that scholars had been waiting for, as it featured the same royal decree written in three different scripts: hieroglyphs, Demotic, and Ancient Greek.
- In 1822, the real breakthrough in solving this mystery came thanks to a brilliant French scholar named Jean-François Champollion.
- By comparing Greek royal names such as Ptolemy and Cleopatra with the symbols inside the cartouches—the oval shapes surrounding royal names—he was finally able to crack the code.
- This discovery marked the long-awaited turning point, unlocking an entire history and allowing a great civilization to be understood once again.
Suddenly, the silent walls of the temples could “speak” again. For the first time, scholars were able to read the names of the pharaohs, understand their laws, and hear their prayers in their own words. Without that single stone and Champollion’s relentless dedication, the world of Ancient Egypt might have remained a mystery forever.
Why Are Hieroglyphs Important Today?
Some people believe that hieroglyphics matters only to professors and historians, but in reality, it is one of our most powerful windows into the human side of Ancient Egypt.
Without hieroglyphics, ancient Egyptian monuments would feel empty and almost meaningless. The Egyptians recorded everything through writing—from complex religious beliefs and spiritual ideas to everyday details, such as how much grain was stored in a warehouse.
Thanks to hieroglyphics, we can truly “hear” the voices of ancient Egyptians today. We learn about their political struggles, their love poems, and even their personal concerns about death and the afterlife.
Anyone who visits Egypt with even a basic understanding of how hieroglyphics works can immediately feel the difference. The experience becomes deeper, more meaningful, and far more magical than simply viewing the monuments without this knowledge.
Instead of seeing only “pretty carvings” on a temple wall, you begin to recognize the names of famous kings, such as Ramesses, or identify symbols connected to life, protection, and power.
Understanding hieroglyphs transforms a silent monument into a living story. It connects us directly to the past and reminds us that the people who built the pyramids were not just names in history books, but real individuals with stories they wanted the future to remember.
Are Hieroglyphs Still Used?
No, hieroglyphs are no longer used as a functional writing system for daily communication. However, they remain highly active in the fields of archaeology, education, and tourism. You will also see them widely used in modern Egyptian art, jewelry, and as a core element of the country’s cultural identity in museums and historical sites.
Although hieroglyphics is not used in everyday life in Egypt today, this does not mean that it is “dead.” The script has not disappeared; instead, it has transformed from a practical writing tool into a powerful symbol of heritage and identity.
In Egypt, hieroglyphs still appear everywhere—from the logos of major companies to beautifully crafted gold jewelry sold in places like Khan el-Khalili. Over time, they have become a visual shorthand for “Egypt,” instantly recognizable around the world.
At the same time, scholars and students across the globe continue to spend years learning how to read hieroglyphics. Their work allows ancient Egyptian texts to be translated and understood, especially as new discoveries continue to emerge from the desert sands.
Frequently Asked Questions About Hieroglyphics
Is hieroglyphics a language?
Technically, hieroglyphics is the writing system, while the language itself is known as Ancient Egyptian. It’s a bit like how we use the Latin alphabet to write English; the symbols are the “code” used to put the spoken language onto stone or papyrus.
How many hieroglyphs are there?
In the early days, there were about 700 to 800 common signs. However, by the time the Greeks and Romans arrived in Egypt, the number had exploded to over 5,000. This was partly because priests wanted to make the texts more complex and “secret.”
Can hieroglyphs be translated?
Yes, absolutely. Ever since the Rosetta Stone was decoded in the 19th century, scholars have been able to translate hieroglyphs with a high degree of accuracy. Today, we can read everything from royal decrees to personal letters and religious spells.
Are hieroglyphs pictures or letters?
They are actually both. Some signs represent a whole word or idea (like a picture), while others represent a specific sound (like a letter). Most words are spelled out using a combination of both types of signs to make the meaning clear.
Conclusion
Hieroglyphs are far more than a dead script from a lost world. They are a direct link to the hearts and minds of the people who built some of the most extraordinary monuments on Earth.
When you understand even a little of how hieroglyphs work, the carvings on temple walls stop feeling “mysterious” and begin to feel personal. You realize that you are looking at the very same symbols a scribe carefully carved thousands of years ago, hoping that someone in the distant future would pause and read them.
There is truly no substitute for seeing these carvings in person. Standing in the shadow of a massive temple wall in Luxor, or leaning closer to study the fine details on a sarcophagus inside a museum, is a completely different experience from viewing them in photographs. It is a chance to walk through history and see the world through ancient Egyptian eyes.
If you are planning a trip to Egypt, keep an eye out for cartouches and sacred birds carved into the stone. Once those symbols begin to speak to you, the magic of the ancient world truly comes alive.
Reading about hieroglyphs is fascinating—but seeing them carved into temple walls is something else entirely. Standing before these ancient symbols in their original setting transforms history into a living experience, where stories, prayers, and names carved in stone finally come to life.
If you’re ready to explore Egypt with deeper understanding and meaning, Egypt Tours Group is here to help you experience these ancient wonders the right way.