What Continent Is Egypt In? Africa, Asia, and the Truth Behind the Map
Ask anyone, “What continent is Egypt in?” and they’ll probably shout out “Africa” without a second thought. And they’re mostly right, but Egypt is one of those rare, tricky places that doesn’t like to stay inside the lines. It’s actually a transcontinental country, meaning it’s got one foot in Africa and the other in Asia. It’s basically the world’s most famous land bridge, sitting right where two massive continents meet, which is why the answer isn’t always as simple as a one-word label.
This “split personality” geography is exactly what makes the place so interesting. You’ve got the vast majority of the country sitting in Northeast Africa, but then you cross the Suez Canal, and suddenly you’re in the Sinai Peninsula, which is technically Asia.
It’s a detail that has shaped everything from ancient trade routes to modern-day travel vibes. We’re going to dig into the map, clear up the confusion about where Africa ends and Asia begins, and look at why being stuck between two continents is actually Egypt’s greatest strength.
What Continent Is Egypt In?
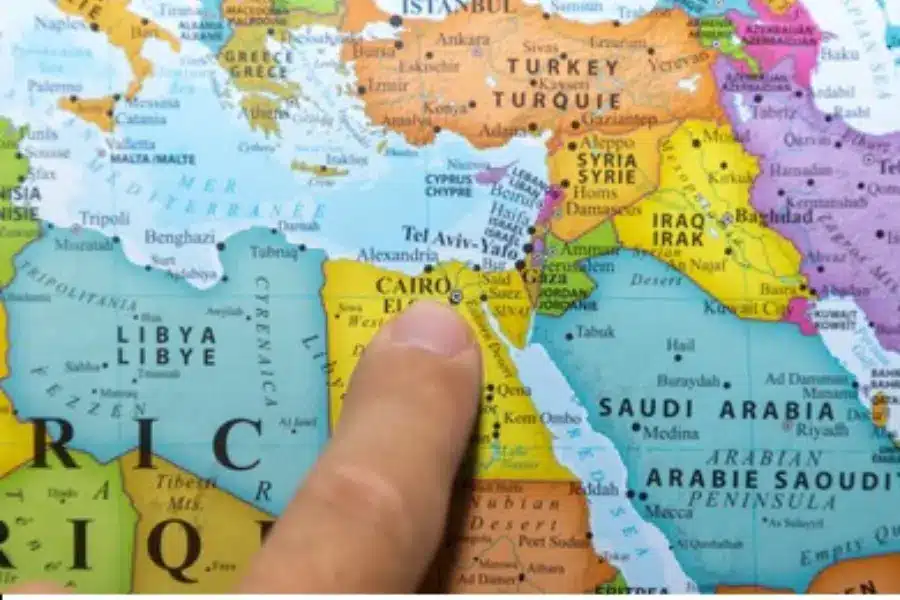
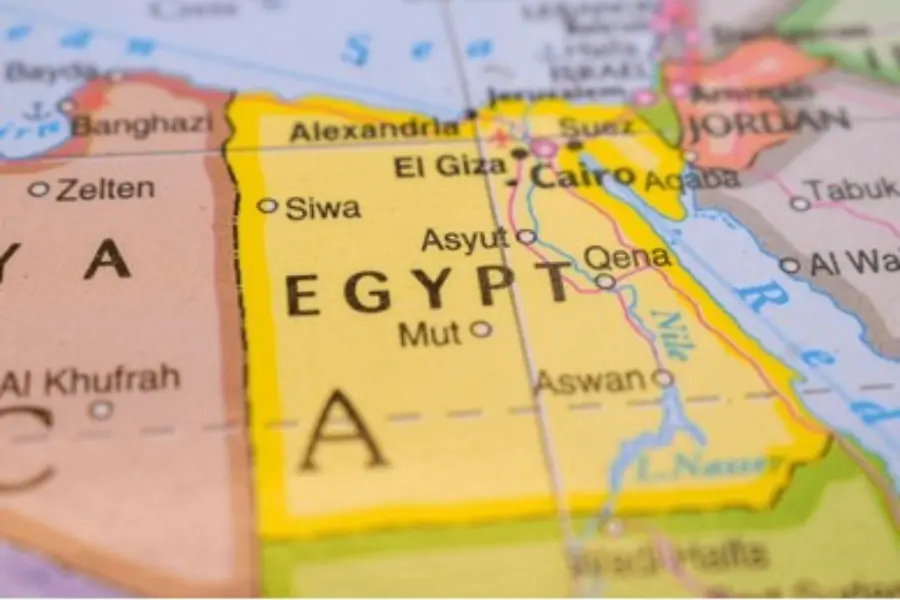
What continent is Egypt in? Egypt is primarily located in the northeast corner of Africa. However, it is a transcontinental country, as its Sinai Peninsula is geographically situated in Western Asia. This unique position makes Egypt a bridge between the two continents, though the vast majority of its land and population are in Africa.
It’s funny how often people find themselves asking, “ In what continent is Egypt? ” even after seeing it on a map a dozen times. The confusion usually stems from the fact that Egypt is so deeply tied to the Middle East, which is a region most people associate strictly with Asia.
Because of this cultural and political connection, it’s easy to forget the physical geography. When you look at the actual borders, Egypt is in what continent becomes a “two-part” answer. Most of the country is firmly rooted in Africa, but that small slice of land to the east changes the whole definition.
Is Egypt in Africa or Asia?
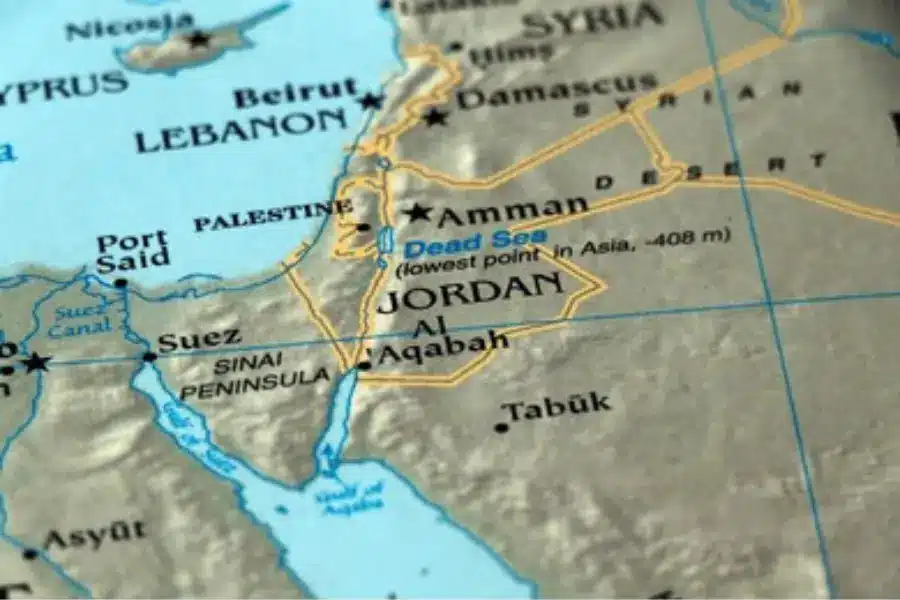
Is Egypt in Africa or Asia? Egypt is technically in both. While about 94% of the country’s landmass is in North Africa, the remaining 6% representing the Sinai Peninsula, is located in Asia. The Suez Canal serves as the modern geographical boundary that separates the African side of Egypt from its Asian territory.
So, the real debate of “ is Egypt in Africa or Asia” isn’t about which one is “right,” but how the country manages to be both at once. Think of it this way: the Nile Valley, Cairo, and the famous pyramids are all on the African side. But once you cross over the Suez Canal into the Sinai, you’ve technically stepped onto a different continent.
This canal isn’t just a massive shipping lane; it’s the official dividing line. It’s a rare geographical setup that gives Egypt a foot in two worlds, blending African roots with a direct physical link to the heart of the Middle East.
Key points:
- Nile Valley, Cairo, and pyramids = African side
- Crossing Suez Canal = steps into Asia
- Canal = official dividing line
- Egypt has a presence in two continents
- Blends African roots with link to Middle East
Where Exactly Is Egypt Located on the Map?
If you were to look at an Egypt location map, you’d see Egypt is tucked into the very top-right corner of Africa. It’s a pretty strategic spot, honestly. To the north, the country is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea, which has connected Egypt to Europe and the rest of the ancient world for thousands of years.
Then, if you look to the east, you’ve got the Red Sea, famous for its incredible diving and its role as a gateway to the Indian Ocean. It’s this specific placement that is sandwiched between these two massive bodies of water, and also has made Egypt a global hub since the dawn of civilization.
When people ask, “ Where is Egypt located?”, they often forget just how much of a “cornerstone” it is. To the west, you have the vast stretches of the Sahara Desert in Libya, and to the south, the Nile flows up from Sudan.
The country is basically a massive rectangle of desert, but it’s split right down the middle by the green ribbon of the Nile River.
This geography is what defines the Egyptian experience; you have the lush, crowded life along the riverbanks surrounded by endless miles of golden sand, all sitting at the perfect meeting point of Africa and the Mediterranean world.
Why Is Egypt Considered a Transcontinental Country?
What is a transcontinental country? A transcontinental country is a nation that occupies land on more than one continent. Egypt fits this definition because while the majority of its territory is in North Africa, the Sinai Peninsula is geographically part of Western Asia, making Egypt a bridge between the two continents.
The term transcontinental country might sound like something strange or out of the geography textbook, but it’s actually a pretty cool way to describe Egypt’s “double life.”
It means the country isn’t confined to just one continental plate. While most of the world’s nations are tucked nearly into one continent, Egypt, along with a few others like Turkey or Russia, breaks the line.
This Egypt continent Africa Asia split isn’t just a technicality; it’s a major part of the country’s identity. It’s the reason why Egypt feels like the heart of the Arab world while still being firmly rooted in African soil.
Why is Egypt a transcontinental country?
- Egypt fits the definition of a transcontinental country.
- The majority of its territory is in North Africa.
- The Sinai Peninsula is geographically part of Western Asia.
- Egypt acts as a bridge between the two continents.
Think about it this way: while a country like Turkey has a city (Istanbul) that splits two continents, Egypt has an entire massive peninsula -the Sinai Peninsula- that lies in Asia. This isn’t just a fun fact for a map; it’s a huge deal for how the country works. It means Egypt is literally the only place on Earth where you can drive across a bridge or through a tunnel and find yourself on a completely different continent in minutes. This “bridge” status is exactly why Egypt has been such a powerhouse for thousands of years, it’s the only spot where Africa and Asia actually touch, and that gives the country a vibe you just won’t find anywhere else.
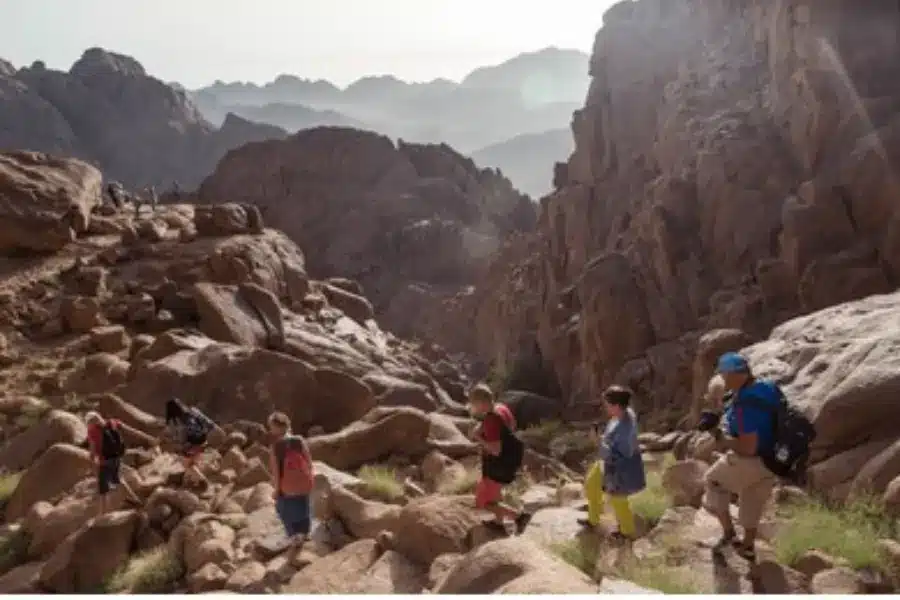
The Sinai Peninsula: Egypt’s Asian Side
When you cross the Suez Canal, you’re not just moving to a different part of the country, you’re technically stepping into Asia. The Sinai Peninsula is this massive, triangular piece of land that acts as the only physical link between Africa and the rest of the world.
Geographically, it’s entirely Asian, but historically and politically, it has been the heart and soul of Egypt for thousands of years. It’s a rugged, beautiful place that feels completely different from the lush Nile Valley, dominated by red granite mountains and vast, sweeping deserts that have seen everything from ancient armies to wandering pilgrims. The importance of the Sinai is hard to overstate.
From a religious standpoint, it’s home to Mount Sinai, where the history of the world was changed forever. Strategically, it’s the gateway to the East, a piece of land that has been fought over and defended since the time of the Pharaohs.
But for travelers today, it’s also a world-class destination. Whether you’re diving in the crystal-clear waters of Sharm El Sheikh or trekking through the mountains of St. Catherine, you’re experiencing the “Asian side” of Egypt. It’s this mix of deep spiritual history and stunning natural beauty that makes the Sinai such a vital part of what Egypt is today.
Ancient Egypt and Its African Identity
One question that comes up a lot in history classes is “ What continent is ancient Egypt in?”, and the answer is deeply rooted in the soil of Africa. While Egypt has always been a crossroads, its ancient civilization was born from the rhythm of the Nile River, which flows from the heart of the African continent.
The Pharaohs didn’t see themselves as separate from Africa; their entire world was built around the seasonal flooding of the river that brought life to the desert. From their architecture to their religious beliefs, the roots of Ancient Egypt are firmly planted in African geography and culture.
It’s important to realize that Ancient Egypt was an African powerhouse long before the modern borders of “continents” were even drawn. Their trade routes reached deep into the African interior, bringing in gold, incense, and exotic woods that fueled the luxury of the royal courts.
When you look at Giza Pyramids or the temples of Luxor, you’re looking at the peak of an African civilization that mastered its environment like no one else. Even though Egypt is a bridge to Asia today, its soul and its history will always be tied to the African continent and the great river that made it all possible.
Egypt Between Africa and the Middle East
It’s easy to see why people get a bit twisted up when they try to label Egypt. You’ll hear it called an African country one minute and a Middle Eastern one the next. The trick is realizing that “Africa” is a physical continent, while the “Middle East” is more of a political and cultural grouping.
Egypt is the perfect example of how those two things overlap. Geographically, it’s sitting on the African continent, but culturally, linguistically, and politically, it’s the heavy hitter of the Middle East.
This is why you’ll almost always see it grouped into the “MENA” region, which just stands for Middle East and North Africa.
Being part of MENA basically means Egypt shares a lot of its modern identity with its neighbors in Asia, like Jordan or Saudi Arabia, even though it’s physically in Africa. It’s about the shared language, the history of the Islamic world, and the deep economic ties that bind these countries together.
So, when you’re looking at a map, you’re looking at Africa. But when you’re looking at the news or cultural trends, you’re looking at the heart of the Middle East.
It’s this dual identity that makes Egypt feel so much larger than just its borders; it’s a country that manages to lead an entire region while staying firmly rooted in its own continental soil.
Why Knowing Egypt’s Continent Matters for Travelers
If you’re a first-time visitor, you might think that knowing which continent Egypt is in is just a bit of trivia, but it actually changes what you should expect from your trip.
Egypt doesn’t really fit the “typical” image people have of either Africa or Asia.
If you’re coming from a safari in East Africa, the bustling, Mediterranean-style streets of Alexandria or the massive urban sprawl of Cairo will feel like a totally different world.
On the flip side, if you’ve just spent time in the ultra-modern cities of the Gulf in Asia, the ancient, dusty charm of Luxor and the deep-rooted traditions of the Nile Valley will offer a much more “historic” vibe.
The climate is another big factor that’s tied to its location. Being in the northeast corner of Africa means you’re dealing with a desert climate that’s influenced by both the Mediterranean and the Red Sea.
It’s not the tropical heat you might find further south in Africa, nor is it exactly the same as the humid coasts of Asia. Understanding this “in-between” geography helps you pack right and plan your itinerary better.
You’re getting a mix of African landscapes and Middle Eastern culture, which means your experience will be a unique blend that you can’t really find anywhere else. It’s that specific “crossroads” energy that makes a trip to Egypt feel like you’re visiting two continents for the price of one.
Common Misconceptions About Egypt’s Location
Common Myths About Egypt’s Geography
Myth 1: Egypt is entirely in Asia
A lot of people assume this because Egypt is deeply connected to Middle Eastern culture and politics. But geographically, this isn’t true at all. About 94% of Egypt lies in Africa, while only a small portion is in Asia.
Myth 2: The Middle East is a continent
This is one of the biggest sources of confusion. The Middle East isn’t a continent—it’s a cultural and political region that stretches across both Africa and Asia. So being “Middle Eastern” doesn’t automatically mean being Asian.
Myth 3: Africa is only Sub-Saharan
Many people picture Africa as jungles, savannas, or wildlife documentaries. When they see Egypt’s Mediterranean coast, deserts, or cities like Alexandria, it doesn’t match that mental image—so they assume it can’t be Africa.
In reality, Africa is incredibly diverse, and North Africa has its own Mediterranean character, with Egypt as one of its clearest examples.
It’s honestly easy to see why people get confused when trying to place Egypt on a map. Because Egypt plays such a major role in Middle Eastern culture and politics, many people subconsciously place it in Asia. But culture doesn’t always match geography.
You can be fully Middle Eastern in language, history, and identity while standing firmly on African soil—and that’s exactly the case for most of Egypt.
Then there’s the Sinai factor. Some people hear that Egypt has land in Asia and assume the whole country must be there. In reality, that Asian portion—the Sinai Peninsula—makes up only about 6% of Egypt’s land. It’s important, yes, but the heart of the country—the Nile, Cairo, and the vast majority of the population—is entirely African.
Understanding these myths matters because Egypt isn’t something you can neatly place in one box. It’s African by geography, Middle Eastern by culture, Mediterranean by history—and that unique mix is exactly why Egypt has been a crossroads of civilizations for thousands of years.
| Feature | Detail |
|---|---|
| Myth | Reality |
| Egypt is entirely in Asia | 94% of Egypt is in Africa; only the Sinai Peninsula (~6%) is in Asia |
| The Middle East is a continent | The Middle East is a cultural and political region, not a continent |
| Africa is only Sub-Saharan | Africa includes the Mediterranean landscapes of the north, including Egypt |
Frequently Asked Questions About Egypt’s Continent
What continent is Egypt in?
Well, it’s Africa, mostly. But it’s not that simple because of the Sinai Peninsula, which is actually in Asia. So yeah, Egypt is one of those rare places that’s technically in two continents at the same time.
Is Egypt in Africa or Asia?
Both, really. About 94% of the land is on the African side, and the other 6% is in Asia. The Suez Canal is the big divider there. It’s pretty cool; you can basically switch continents just by crossing a bridge.
Is Cairo in Africa or Asia?
Cairo is definitely in Africa. It’s on the west side of the canal, right by the Nile. Even though it’s a huge Middle Eastern hub, geographically, you’re still in Africa when you’re there.
What continent was ancient Egypt in?
It was African. Everything about the Pharaohs was tied to the Nile, which comes from the heart of Africa. They did some stuff in Asia, sure, but their home was always Africa.
Conclusion
Egypt’s Unique Position Between ContinentsHonestly, trying to label Egypt as just “one thing” is kind of a waste of time. The whole point of the place is that it’s a bridge.
It’s where Africa and the Middle East just… meet. You’ve got the Nile on one side and the Sinai on the other, and that mix is what makes it so different from anywhere else you’ll ever visit.
If you’re thinking about going, just know that you’re not just visiting a country; you’re visiting a crossroads. It’s got this weird, amazing blend of African roots and Middle Eastern vibes that you just can’t find on a regular map.
It’s been that way for thousands of years, and that’s exactly why it’s still so fascinating today.
Egypt isn’t just a place on the map — it’s a journey through Africa and the Middle East at the same time. From the Nile Valley and ancient temples to the Sinai’s mountains and Red Sea beaches, every step tells a different story.
Explore our carefully designed Egypt tours and experience the crossroads of continents for yourself.